Gametogenesis:
Gametogenesis is the process of formation and development of haploid gametes from the diploid germ cells in the gonads of sexually reproductive organism.
Gametogenesis can be of two types; spermatogenesis in male and oogenesis in female.
Phases Of Gametogenesis:
Phases of gametogenesis though it may be spermatogenesis or oogenesis both are proceed through three phases;
a) Multiplication phase
b) Growth phase
c) Maturation phase
i) Spermatogenesis:
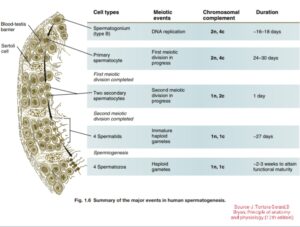
Spermatogenesis is the process of production of spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testes by attainment of puberty in male. Spermatogenesis can further divided into two consecutive events which are as follows;
1.Formation of spermatid and
2.Spermiogenesis.
1.Formation of spermatid:
At the base of seminiferous tubules epithelium spermatogonial stem cells are present which on divide mitotically gives rise to Type A Spermatogonia which again gives rise to Type B Spermatogonia. Generally this phase is considered as the multiplication phase.
In growth phase Type B spermatogonia proliferate in few numbers which gives rise to primary Spermatocytes. The primary Spermatocytes in maturation phase undergo two consecutive meotic division in first meotic division the primary Spermatocytes give rise two secondary Spermatocytes,which on further division produces two haploid Spermatids.
2. Spermeogenesis:
After the formation of spermatid it does not divide further,rather it undergoes a series of transformation to attain the cell type called Spermatozoa (singular- spermatozoon). The process of formation of spermatozoa from spermatid is called Spermeogenesis.
During the transformation different categorical changes happens in spermatozoa like reduction in size of nucleus and condensation of chromosomal material. At the frontal end of nucleus golgi apparatus give rise to acrosome,the shape of nucleus became elongated. The acrosomal end of the head is filled with enzyme which play a crucial role in fertilization process. Axial filament of the centriole grows out to form flagellum having the basic structure (9+2) arrangement i.e pair of longitudinal ring fibre surrounded by nine fused pair of microtubules. Mitochondria are present to proximal part of the flagellum which provides energy for movement of sperm. After the maturation spermatozoa is rightly ready to act as sperm cells consisting of a head containing nucleus and acrosome; a middle piece containing the centrioles,proximal part of flagellum and mitochondria helix and lastly the end part is tail which consist of a flagellum.
ii) Oogenesis:
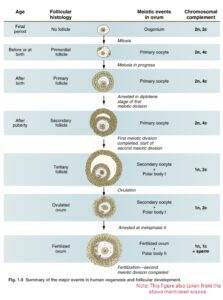
Oogenesis is quite complicated and lengthy in comparison to the process of spermatogenesis. It can be also divided into three consecutive events as ;
1) Multiplication phase
2) Growth phase and
3) Maturation phase.
Unlike spermatogenesis the process of oogenesis in females begins before they born.
During the phase of multiplication which is occurs during early fetal development the primordial germ cells differentiate to produce oogonia which is diploid in nature;it divide mitotically to produce numbers of oogonia.
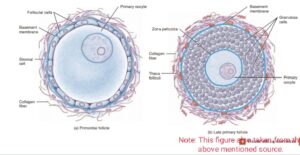
The growth phase is designated by the formation of larger cells called primary oocytes,which undergo meotic division and arrested in prophase -1 stage.During this phase each primary oocyte is surrounded by a single layer of flat follicular cells and it becomes primordial follicle.
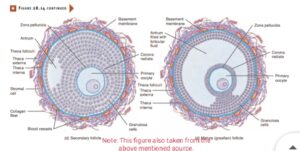
After attainment of puberty due to role play by gonadotropins i.e FSH and LH the development of several primordial follicles takes place,amongst them only one will luckly reach to the maturation phase.During this maturation phase each primordial follicles starts growing and becomes primary follicle .The primary follicle contain a primary oocyte which surrounded by several layer of cells called granulosa cells. As the process of maturation goes on a glycoprotein layer called zona pellucida will form in between primary oocytes and granulosa cells. With ongoing process of maturation by developing different theca layer the primary follicles becomes secondary follicles and further it becomes larger one called mature graafian follicle.
The mature graafian follicles where the primary oocytes present complete the meosis-I and produce haploid unequal cells i.e a larger secondary oocytes and a smaller first polar body. After the formation of secondary oocytes it starts meosis-II and restrict in metaphase ,at the time of LH surge the mature graafian follicle rupture and it releases the secondary oocytes along with first polar body the process is called ovulation.
The meosis-II resumes and get complete whenever the sperm penetrates the secondary oocytes. Entry of sperm causes division of secondary oocytes into haploid unequal cells called a larger ovum and a smaller second polar body. If the first polar body undergoes division it produces two polar bodies; and ultimately three polar bodies and one mature egg will produce at the end of oogenesis,but all the polar bodies get degenerates having an ovum as the final constituent of oogenesis.
👍
Thank you
👍🏻👍🏻👍🏻
Thank you